This is how a Bill becomes a Law in the Australian Parliament
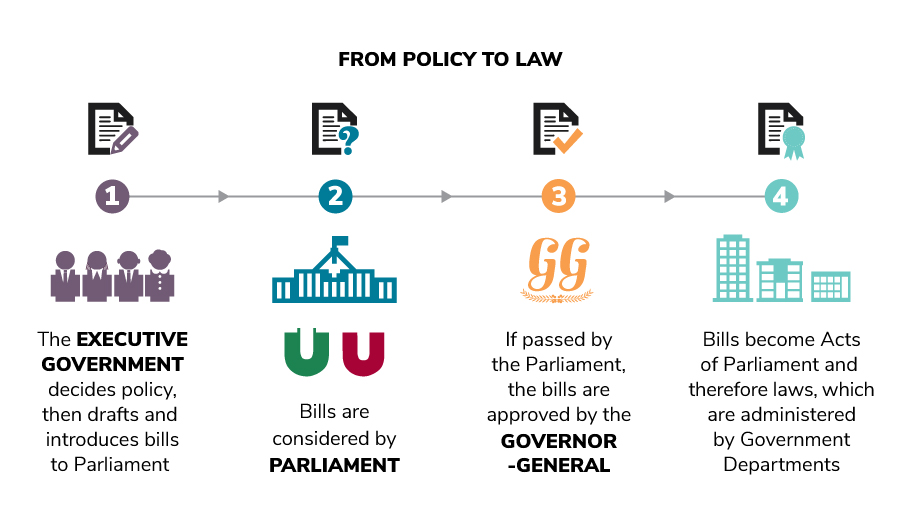
The process first begins in the Executive Government where bills are decided on and drafted. The Exec Gov decides laws, then drafts and introduces bills to Parliament. Other parties and Independents can also introduce bills. The bills that are introduced to parliament are decided in Cabinet meetings between the Prime Minister and senior ministers.
The next step is for the bill to be approved by the House of Parliament. Members of Parliament then make speeches which voice their opinion on whether they agree or disagree with the bill. The House of Representatives (along with the Senate) can decide to send the bill to a committee for learn more about it. The committee seeks information about the bill from members of the community, experts and interest groups. The committee forms a report on their findings to be presented to the House of Representatives based on evidence from their investigation.
The members vote with an AYE or NO and if the result is not clear, the members will be requested to either move to the right or the left of the speakers/presidents chair to vote yes or no. The members can then debate and make amendments to the bill.
Once the bill has passed the House of Representatives it goes to the Senate and a very similar process takes place.
Once the bill has passed the House of Representatives and the Senate, it has to be given the Royal Asssent by the King's representative, the Governor-General. The bill then becomes Acts of Parliament and needs to be put into action by the departments (i.e Department of Education). The departments would need to inform the people affected by the laws, organise social media campaigns, ads and news articles.